Description:
All about Information Technology infrastructure and system. Helpdesk & support issue, deployment guide, and daily activity in managing an information technology operation.
Search This Blog
Tuesday, January 2, 2024
Another Error code 0x80070643 when installing Microsoft Defender for Identity sensor
Monday, September 25, 2023
Cannot Install PowerShell Module - Unable to find module repositories
Description:
You try to Install a new PowerShell Module. But you got an error saying "No match was found for the specified search criteria and module name ' ' Try Get-PSRepository to see all available registered module repositories". However when you try to run Get-PSRepository command you got "Unable to find module repositories error".
You have try the following, but still have the problem:
- Make sure to Run as Administrator,
- Make sure to use TLS 1.2
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
- Unregister and Register
- Unregister-PSRepository -Name PSGallery
- Register-PSRepository -Default
Thursday, May 20, 2021
Error when Granting Access to the User at tenant root scope “/” to deploy Enterprise-Scale
Description:
You want to deploy Enterprise-Scale Architecture at your Azure Environment.
One of the prerequisite is to explicitly provide roleAssignment (RBAC) at the tenant root scope via CLI or PowerShell (Note: There’s no portal UX to make this roleAssignment)
However several error occurred when you try to run the following command at Azure CLI to provide the role Assignment.
- az login
Error message: The following tenants don't contain accessible subscriptions. Use 'az login --allow-no-subscriptions' to have tenant level access.
- az role assignment create --scope '/' --role 'Owner' --assignee-object-id $(az ad signed-in-user show --query objectId)
Error message: Failed to query --assignee-principal-type for "7786a679-034b-42cc-a23a-xxxxxxxxxxxx" by invoking Graph API. RBAC server might reject creating role assignment without --assignee-principal-type in the future. Better to specify --assignee-principal-type manually. The Principal ID '"7786a679-034b-42cc-a23a-xxxxxxxxxxxx"' is not valid. Principal ID must be a GUID.
Resolution:
To fix the issue, the command needs some small changes. Instead of using the above command, try to use the following command:
- az login -t yourdomainname.onmicrosoft.com
- az role assignment create --scope '/' --role 'Owner' --assignee-object-id "7786a679-034b-42cc-a23a-xxxxxxxxxxx"
Sunday, April 18, 2021
Azure Service Endpoints vs Private Link
Virtual Network (VNet) service endpoint provides secure and direct connectivity to Azure services over an optimized route over the Azure backbone network. Endpoints allow you to secure your critical Azure service resources to only your virtual networks. Service Endpoints enables private IP addresses in the VNet to reach the endpoint of an Azure service without needing a public IP address on the VNet.
Service Endpoints do have some limitations or downsides. Firstly it is key to remember that traffic to a Service Endpoint is still leaving your virtual network, and the Azure PaaS resource is still being accessed on its public address. Service Endpoints cannot be used by traffic originating on-premises, through VPN or Express Route, only for traffic coming from your Azure Virtual Network.
Private Link is a newer solution than Service Endpoints, introduced about a year ago. The key difference between Private Link and Service Endpoints is that with Private Link you are injecting the multi-tenant PaaS resource into your virtual network. With Service Endpoints, traffic still left you vNet and hit the public endpoint of the PaaS resource, with Private Link the PaaS resource sits within your vNet and gets a private IP on your vNet. When you send traffic to the PaaS resource, it does not leave the virtual network.
Private Link also allows access from resources on your on-premises network through VPN or ExpressRoute, and from peered networks. You can also connect to resources across region.
How to choose?
According to https://samcogan.com/service-endpoints-and-private-link-whats-the-difference/
Service Endpoints are more straightforward and easier to set up than Private Link. You can enable Service Endpoints with a couple of clicks in the portal, and there is no requirement for any additional services. Private Link, however, requires you to implement DNS changes and possibly use Azure Private DNS, it also requires deciding where the service will attach to your Virtual Network. So if you need some additional access restriction for your PaaS Services quickly, or don’t have the rights or knowledge to make changes to DNS, then Service Endpoints are probably the way to go.
Other than complexity, Private Link is superior to Service Endpoints in nearly every other way.
Azure Load Balancing
There are various option that Azure provides for load balancing services that you can use to distribute your workloads across multiple computing resources.
- Application Gateway
- Front Door
- Load Balancer
- Traffic Manager
Saturday, April 10, 2021
Azure Private Endpoint, Private Link, and Private Link Service
Azure Private Endpoint
Azure Private Endpoint is a network interface that connects you privately and securely to a service powered by Azure Private Link. Private Endpoint uses a private IP address from your VNet, effectively bringing the service into your VNet. The service could be an Azure service such as Azure Storage, Azure Cosmos DB, SQL, etc.
Azure Private Link
Azure Private Link enables you to access Azure PaaS Services (for example, Azure Storage and SQL Database) and Azure hosted customer-owned/partner services over a private endpoint in your virtual network
Azure Private Link Service
Azure Private Link Service is the reference to your own service that is powered by Azure Private Link. Your service that is running behind Azure Standard Load Balancer can be enabled for Private Link access so that consumers to your service can access it privately from their own VNets. Your customers can create a private endpoint inside their VNet and map it to this service.
ExpressRoute Direct VS FastPath VS Global Reach
ExpressRoute Private Peering VS Microsoft Peering in Azure
Availability Sets VS Availability Zones in Azure
Availability Sets
Availability Sets is for virtual machine only. When you configure virtual machine with availability sets, it will make a copy of your virtual machine in isolated separate physical server, compute rack, storage units and network switches within a single datacentre within an Azure Region.
Availability Zones
Availability Zones can be use by many Azure Services including virtual machine. With Availably Zones, your workload will be spread out across the different zones that make up an Azure region. An Azure region is made up of multiple datacentres and each zone is made up of one or more datacentres. Each datacentre is equipped with independent power, cooling and networking.
Availability Zone has better SLA compare to Availability Sets
Sunday, March 28, 2021
Azure AD Connect account usage
Azure AD Connect uses 3 accounts in order to synchronize information from on-premises or Windows Server Active Directory to Azure Active Directory. These accounts are:
AD DS Connector account: used to read/write information to Windows Server Active Directory
ADSync service account: used to run the synchronization service and access the SQL database
Azure AD Connector account: used to write information to Azure AD
In addition to these three accounts used to run Azure AD Connect, you will also need the following additional accounts to install Azure AD Connect. These are:
Local Administrator account: The administrator who is installing Azure AD Connect and who has local Administrator permissions on the machine.
AD DS Enterprise Administrator account: Optionally used to create the “AD DS Connector account” above.
Azure AD Global Administrator account: used to create the Azure AD Connector account and configure Azure AD.
SQL SA account (optional): used to create the ADSync database when using the full version of SQL Server. This SQL Server may be local or remote to the Azure AD Connect installation. This account may be the same account as the Enterprise Administrator. Provisioning the database can now be performed out of band by the SQL administrator and then installed by the Azure AD Connect administrator with database owner rights.
Cannot Start Azure ATP or Defender for Identity Services when using gMSA
Description:
Make sure you have Restarted the Domain Controllers that you put inside the new universal or domain local group. After the Domain Controller restart, try to login and notice that Azure ATP Sensor Services will be able to start properly. Delayed start is expected for Azure ATP services.
Saturday, March 27, 2021
Error when Configuring Azure AD Connect - Authorization Manager check failed
Description:
When you configure your Azure AD Connect, you encounter Authorization Manager check failed error message.
It said "An error occurred while retrieving the Active Directory Schema. The error are: AuthorizationManager check failed."
Try to manually installing the Microsoft certificate:
- Go to C:\Program Files\Microsoft Azure Active Directory Connect\AdSyncConfig\AdSyncConfig.psm1
- Right click the file, and open properties
- Go to 'Digital Signatures' tab and open the details for the certificate
- Click View certificate
- Click Install certificate for local machine
- Manually choose to store certificates at 'Trusted publishers'
- Click Ok to close the certificate wizard.
- Go Back to the Azure AD Connect Wizard > Click Previous > and Click Next again.
Error when configuring Azure AD Connect at MSOnline.Format.ps1xml file
Description:
When you configure your Azure AD Connect, you encounter Authorization Manager check failed error message.
It said " Unable to retrieve the Azure Active Directory configuration. Errors occurred while reading the format data file: Microsoft.PowerShell, , C:\Program Files\Microsoft Active Directory Connect\AADPowerShell\MSOnline.Format.ps1xml: The file was skipped because of the following validation exception: AuthorizationManager check failed."
Try to manually installing the Microsoft certificate:
- Go to C:\Program Files\Microsoft Azure Active Directory Connect\AADPowerShell\MSonline.Format.ps1xml
- Right click the file, and open properties
- Go to 'Digital Signatures' tab and open the details for the certificate
- Click View certificate
- Click Install certificate for local machine
- Manually choose to store certificates at 'Trusted publishers'
- Click Ok to close the certificate wizard.
- Go Back to the Azure AD Connect Wizard > Click Previous > and Click Next again.
Tuesday, March 2, 2021
Azure Messaging Services Comparison
|
Service |
Purpose |
Type |
When to use |
|
Event Grid |
Reactive programming |
Event distribution (discrete) |
React to status changes |
|
Event Hubs |
Big data pipeline |
Event streaming (series) |
Telemetry and distributed data streaming |
|
Service Bus |
High-value enterprise messaging |
Message |
Order processing and financial transactions |
Azure Monitor vs Azure Log Analytics
Azure Storage Type Differences
The Azure Storage platform includes the following data services:
- Azure Blobs:
A massively scalable object store for text and binary data. Also includes support for big data analytics through Data Lake Storage Gen2.
Blob storage is designed for:
- Serving images or documents directly to a browser.
- Storing files for distributed access.
- Streaming video and audio.
- Writing to log files.
- Storing data for backup and restore, disaster recovery, and archiving.
- Storing data for analysis by an on-premises or Azure-hosted service.
- Azure Files:
Managed file shares for cloud or on-premises deployments.Azure Files offers fully managed file shares in the cloud that are accessible via the industry standard SMB or NFS protocol. Azure file shares can be mounted concurrently by cloud or on-premises deployments.
Azure Files SMB file shares are accessible from Windows, Linux, and macOS clients. Azure Files NFS file shares are accessible from Linux or macOS clients. Additionally, Azure Files SMB file shares can be cached on Windows Servers with Azure File Sync for fast access near where the data is being used.
- Azure Queues:
A messaging store for reliable messaging between application components.Azure Queue Storage is a service for storing large numbers of messages. You access messages from anywhere in the world via authenticated calls using HTTP or HTTPS. A queue message can be up to 64 KB in size. A queue may contain millions of messages, up to the total capacity limit of a storage account. Queues are commonly used to create a backlog of work to process asynchronously.
- Azure Tables:
A NoSQL store for schemaless storage of structured data.Azure Table storage is a service that stores non-relational structured data (also known as structured NoSQL data) in the cloud, providing a key/attribute store with a schemaless design.You can use Table storage to store flexible datasets like user data for web applications, address books, device information, or other types of metadata your service requires.
- Azure Disks:
Block-level storage volumes for Azure VMs.Azure managed disks are block-level storage volumes that are managed by Azure and used with Azure Virtual Machines. Managed disks are like a physical disk in an on-premises server but, virtualized.
Tuesday, February 9, 2021
Error when Upgrading Azure AD Connect version
Description:
When you upgrade Azure AD Connect from a previous version, you might encountered the following error: "Upgrade cannot proceed because the Azure Active Directory connector (b891884f-051e-4a83-95af-2544101c9083) is missing.
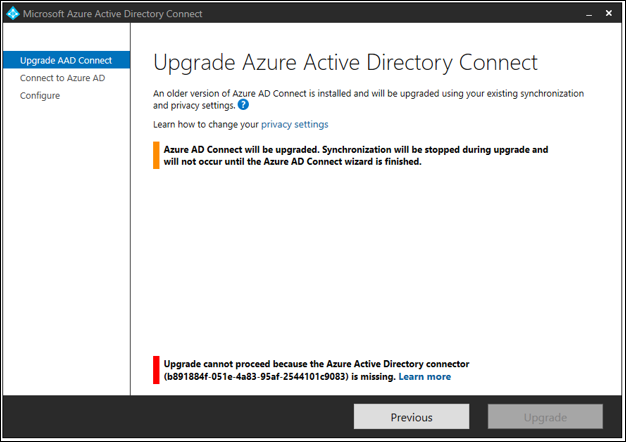
Resolution:
Make sure the PowerShell Execution Policy is set to unrestricted. You can check by running the following command at PowerShell:
Get-ExecutionPolicy
To change the execution Policy to unrestricted, run the following PowerShell command:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
Type Y when asked.
Re-Run the upgrade process again.








